?
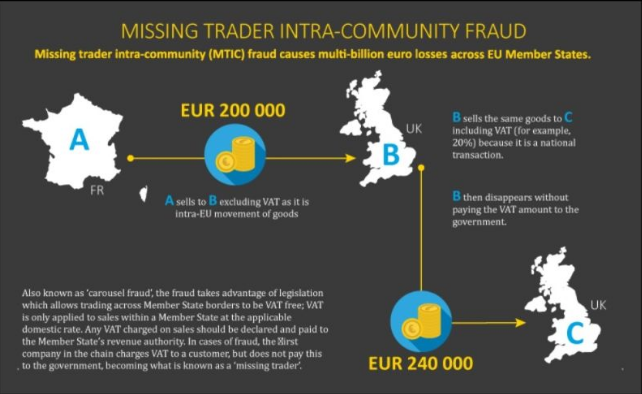
VAT fraud is the theft of value-added tax from a government by organised crime groups (OCG).
The most common scheme is Missing Trader Intra-Community (MTIC) fraud, where criminals take advantage of legislation that allows VAT free trading across EU Member States borders.
In the most complex cases, goods are imported and sold through linked companies before being exported again:
1️⃣ the first company charges VAT to a customer, but does not pay this to the government (missing trader);
2️⃣ the exporters claim and receive the reimbursement of VAT payments that never occurred;
3️⃣ additional “ ” can be interposed, so as to make it more difficult to identify the beneficiary of the fraud.
⚠️ The process can be repeated many times: this is why it is called .
Source Lorenzo Savastano
Latest Posts in "European Union"
- VAT IOSS Scheme: Intermediary Registration Available from April 2026 for Non-EU Businesses
- Customs and VAT Fraud Cost EU €45 Billion in 2025, Officials Warn
- EPPO Investigates Record 3,600 Customs Fraud Cases in 2025, Damages Reach 67 Billion Euros
- Intermediary Registration for UK Import One Stop Shop Scheme Opens April 2026
- EPPO Uncovers €45 Billion VAT and Customs Fraud, Reshaping EU Criminal Landscape in 2025